Perfusion keeps a donated organ alive outside the body, giving surgeons extra time and increasing the number of transplants possible.
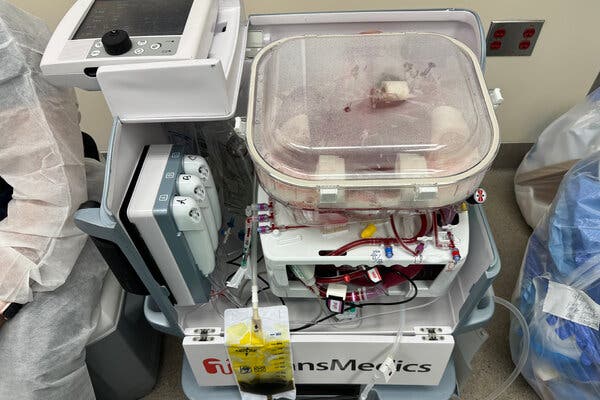
On some level, the human liver in the operating room at Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago was alive. Blood circulating through its tissues delivered oxygen and removed waste products, and the organ produced bile and proteins that are essential to the body.
But the donor had died a day earlier, and the liver lay inside a boxy plastic device. The organ owed its vitality to this machine, which was preserving it for transplantation into a needy patient.
“It’s a little bit science fiction,” said Dr. Daniel Borja-Cacho, a transplant surgeon at the hospital.
Surgeons are experimenting with organs from genetically modified animals, hinting at a future when they could be a source for transplants. But the field is already undergoing a paradigm shift, driven by technologies in widespread use that allow clinicians to temporarily store organs outside the body.
Perfusion, as its called, is changing every aspect of the organ transplant process, from the way surgeons operate, to the types of patients who can donate organs, to the outcomes for recipients.
Most significantly, surgical programs that have adopted perfusion are transplanting more organs.
Since 2020, Northwestern has had a 30 percent uptick in its volume of liver transplants. Nationally, the number of lung, liver and heart transplants each rose by more than 10 percent in 2023, one of the largest year-over-year increases in decades.

